
Figure 1 The structure of the mask
Recently, the COVID-19 epidemic has spread across the world, and masks have become a scarce commodity. The processing of protective masks is inseparable from the mask fabric, and the core of the mask fabric is melt-blown cloth. Although work and production have resumed in China, meltblown cloth, which is at the upstream of mask production, has encountered supply bottlenecks and has become an important factor limiting the growth of mask production capacity in the short term.
Enterprise
I heard that whether a mask is good or not mainly depends on the quality of melt-blown cloth. So what is melt-blown cloth? What is it used for?
Meltblown cloth is the core material of masks. Please listen to my detailed introduction below.
Publisher
Definition and use of meltblown cloth
Melt-blown cloth is the core material of masks. Melt-blown cloth is mainly made of polypropylene as the main raw material, and the fiber diameter can reach 1 to 5 microns. Ultra-fine fibers with many voids, fluffy structure, good anti-wrinkle ability and unique capillary structure can increase the number and surface area of fibers per unit area, thus making the melt-blown cloth have good filtering, shielding, thermal insulation and oil absorption properties. . It can be used in fields such as air and liquid filter materials, isolation materials, absorption materials, mask materials, thermal insulation materials, oil-absorbent materials and wipers. Has many uses:
(1) Medical and sanitary cloths: surgical gowns, protective clothing, disinfection wraps, masks, diapers, etc.;
(2) Cloths for home decoration: wall coverings, tablecloths, sheets, bedspreads, etc.;
(3) Clothing fabrics: linings, adhesive linings, wadding, shaped cotton, various synthetic leather base fabrics, etc.;
(4) Industrial fabrics: filter materials, insulation materials, cement packaging bags, geotextiles, covering fabrics, etc.;
(5) Agricultural cloth: crop protection cloth, seedling raising cloth, irrigation cloth, thermal insulation curtain, etc.;
(6) Others: space cotton, thermal insulation and sound insulation materials, linoleum felt, cigarette filters, tea bags, etc.
Enterprise
How do masks block viruses? How is meltblown cloth produced?
It mainly relies on the mechanical blocking and electrostatic adsorption of the melt-blown cloth in the mask.
Publisher
The protective effect of meltblown cloth
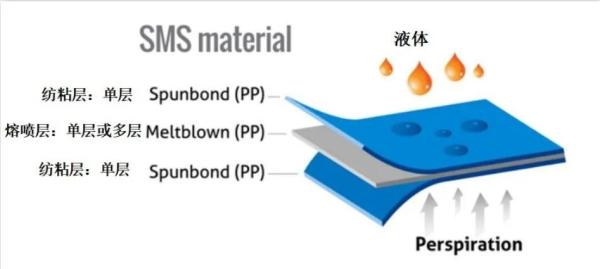
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of SMS non-woven fabric structure
Currently, masks used to protect against viruses are basically non-woven materials. The mask fabrics are composed of spunbond non-woven fabrics and melt-blown non-woven fabrics produced from polypropylene (PP). Medical masks are generally made of three layers of non-woven fabric, as shown in Figure 1. The material is spunbond non-woven fabric + meltblown non-woven fabric + spunbond non-woven fabric, as shown in Figure 2, which is what we call SMS (2 layers of S layers and 1 layer of M layers) structure. Spunbond non-woven fabrics The high strength and small difference in vertical and horizontal strength of (S) and the high shielding and waterproof performance of melt-blown non-woven fabric (M) are combined into one material to form a material with strong waterproof performance, good breathability and high efficiency. Masks with excellent isolation performance.

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of SMS structural blocking and filtering effect
Among them, the "S" and "M" layer materials are:
S represents the spunbond layer (Spunbond). Its fiber diameter is relatively thick, about 20 microns (μm). The outer layer S has the function of blocking dust and water, which can prevent droplets from entering the mask. The inner layer S has the function of absorbing water and can be absorbed. Moisture from the wearer's mouth and nose, 2 layers of S spunbond layer support the entire non-woven structure. The SMS structure blocking and filtering effect is shown in Figure 3.
The middle meltblown layer M (Meltblown) is the most important barrier layer. It is an extremely fine and electrostatically charged meltblown non-woven fabric with a fiber diameter of about 2 microns (μm). It is resistant to dust, flying particles containing bacteria and viruses. When foam comes close to this kind of melt-blown non-woven fabric, it will be electrostatically adsorbed on the surface of the melt-blown fabric and cannot pass through. Since suspended particles such as dust are captured by ultra-fine electrostatic fibers, they are extremely difficult to detach due to cleaning, and washing with water will destroy the static dust-collecting ability. Therefore, this kind of mask can only be used once.
The production process of meltblown cloth
01
The production process of meltblown cloth
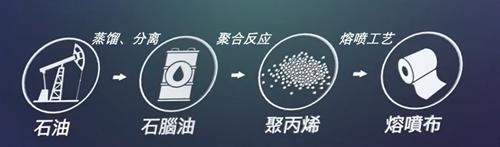
Figure 4 The production process of melt blown cloth
Melt-blown cloth does not look special, but the production process is very complicated. The production process can be summarized into three major links: first, naphtha is extracted from petroleum, then chemically processed into polypropylene, and finally the cloth is made through the melt-blown process. shape object, the general process is shown in Figure 4.
02
The production process of meltblown cloth
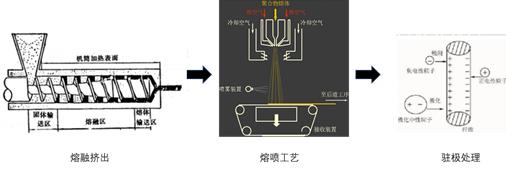
Figure 4 Production process of melt blown cloth
The production process of melt-blown cloth is mainly divided into three steps: melt extrusion, melt-blown process and electret treatment. The specific process diagram is shown in Figure 5. Here we focus on electret processing.
Electret refers to a dielectric material with the function of long-term charge storage. It has the advantages of high efficiency, low flow resistance, antibacterial, energy saving, etc. It not only ensures the physical collision blocking effect of conventional filter materials, but also adds electrostatic adsorption. The electret treatment makes the filter material fibers charged. Combined with the dense characteristics of the melt-blown ultrafine fiber material, a large number of electrodes are formed between the charged fibers. The charged fibers can not only attract most of the charged particles in the environment like a magnet, but also It can polarize some of the uncharged particles to adsorb some pollutants with smaller particle sizes. Even nanoscale substances such as viruses can be electrostatically adsorbed or blocked by charge repulsion.
The meltblown cloth used in medical masks must be electret treated. Sterile medical masks are sterilized with ethylene oxide. After sterilization, there will be ethylene oxide residue on the mask, which not only irritates the respiratory tract, but also contains carcinogens. The residual ethylene oxide must be released through analysis to reach safe content standards. The entire standard analysis and disinfection process takes 7 days to half a month.
Enterprise
What kind of meltblown cloth is qualified?
Generally, samples need to be taken and sent to a qualified laboratory for testing, and eligibility is determined based on the test results.
Publisher
●Testing basis for meltblown cloth
1. According to standards
FZ/T 64034-2014 Spunbond/meltblown/spunbond (SMS) nonwoven fabrics
2. Test items
1
Appearance quality inspection: cloth surface appearance, holes, impurities, odor, micropores, crystal points, frit, stiff threads, unreinforced area, thin mesh, width deviation, color difference, joint quality
2
Intrinsic quality testing: mass deviation rate per unit area, longitudinal breaking strength, transverse breaking strength, longitudinal and transverse breaking elongation, hydrostatic pressure, air permeability
3
Detection of microbial indicators: Announcement of total bacterial colonies, total fungal colonies, coliforms, and pathogenic pyogenic bacteria
Contributed by Jinan Customs
Review/Commodity Inspection Department of the General Administration of Customs